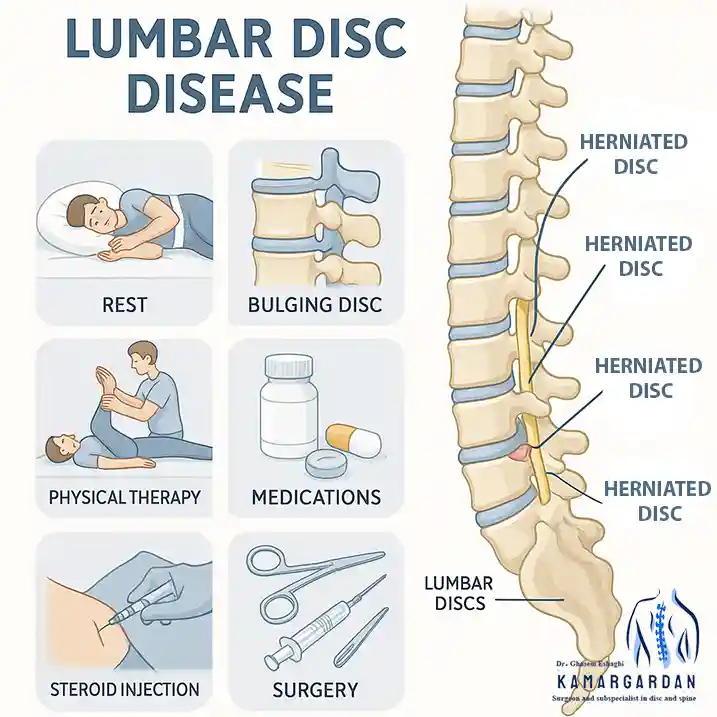
The treatment for lumbar disc disease involves a range of approaches aimed at reducing pain and symptoms related to the condition, as well as improving the quality of life for the affected individual. The most effective methods for treating lumbar disc disease include:
- Rest: Resting in positions that do not exacerbate severe or unbearable pain can help reduce pressure on the disc.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and physical therapy techniques, such as strengthening back muscles, stretching, and corrective exercises, can help strengthen the back muscles and reduce pressure on the disc.
- Behavioral Education: Educational treatments to improve attitudes and daily behaviors that might increase strain or tension can be beneficial.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pain relievers, and corticosteroids may help reduce inflammation and pain. Medication should always be prescribed by a doctor.
- Injections: Local injections, such as steroids or anti-inflammatory substances, may be effective in reducing inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, or when conservative treatments fail, surgery may be considered. In lumbar disc surgery, the damaged portion of the disc is repaired or removed.
The specific treatment plan should be determined by a specialist depending on the severity of symptoms, and the patient should follow the doctor's advice accordingly.
Types of Lumbar Disc Disease and Their Treatments
- Functional Disc Dysfunction: In this type, the disc does not function properly even though there is no structural problem visible on MRI. Patients often experience sciatic pain or back pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Discs that have lost water content are shown as "dehydrated" on MRI, appearing black, unlike healthy discs which appear gray. These are called degenerated or black discs.
- Cracked Discs: These discs develop cracks in their outer ring. The cracks may be longitudinal, transverse, or radial, similar to a car tire.
- Bulging Discs: A healthy disc has a bean-shaped cross-section, with the center being more concave than the edges. When the disc bulges, it is as though the "mortar" between two vertebrae pushes outward.
- Herniated Discs: In this case, the outer ring of the disc tears, and the soft inner material starts to push out into the spinal canal, causing nerve compression. This is also referred to as a disc prolapse.
- Loss of Disc Height: In this condition, the disc's height decreases, and instead of the disc appearing normal on CT scan, air is seen. This is due to the disc's degeneration, and it often causes narrowing of the spinal canal along with bone spurs pressing on nerve roots.
Worst Case of Lumbar Disc Disease
The most severe form of lumbar disc disease is a "herniated disc" or "slipped disc." In this case, the soft inner material of the disc leaks through the outer ring and exerts significant pressure on the spinal nerves.
Symptoms of this severe type of disc disease include intense pain, nerve compression, muscle weakness, spasms, and restricted movement. It may interfere significantly with daily activities and reduce quality of life.
Treatment for severe lumbar disc disease includes rest, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, pain-relief measures such as heat or cold compresses, steroid injections, and surgery if symptoms persist despite other treatments.
Best Methods for Treating Lumbar Disc Disease
The best treatment methods for lumbar disc disease include physical therapy and strengthening exercises. These exercises, along with stretching and corrective techniques, strengthen the back muscles and reduce the strain on the disc. In more severe cases, injections, pain relievers, and surgery may be necessary. Consulting a specialist will help determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
What is Good for Lumbar Disc Disease?
There is no specific food known to cure lumbar disc disease, but certain natural remedies have been suggested. For example, turmeric has been traditionally used in ancient medicine. It is well known for its anti-inflammatory properties and as a powerful antioxidant. Turmeric supplements, specifically curcumin, are available for patients today.
Another beneficial herbal remedy for disc herniation is Devil's Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens), which is available as a pharmaceutical supplement under the name Tantalus.
Treatment for Lumbar Disc Disease at L5
The human lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae, labeled L1 to L5, with the L5 vertebra being located above the sacrum (S1). The disc between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the sacrum is referred to as the L5-S1 disc.
The treatment for L5-S1 disc disease includes anti-inflammatory medications such as diclofenac, ibuprofen, or meloxicam, muscle relaxants like methocarbamol or tizanidine, and sometimes diazepam. Medications like pregabalin or gabapentin, which slow the transmission of pain signals from the spine to the brain, are also prescribed. Wearing a back brace for immobilization can help treat L5 disc disease.
If conservative treatments do not provide relief, treatments such as epidural steroid injections or laser surgery may be considered.
Duration of Lumbar Disc Disease Treatment
The total treatment duration for lumbar disc disease generally spans one to two months. In most cases, patients should experience improvement within this time frame with conservative treatment. If the patient does not improve, surgery may be required.
Surgery is often highly effective if performed at the right time. When the disc is damaged, not only the disc but also other structures such as the facet joints can be affected. Delaying surgery may reduce the chances of a successful outcome.
Is There a Permanent Cure for Lumbar Disc Disease?
There is no definitive cure for lumbar disc disease. Approximately 20% of patients with lumbar disc disease do not recover completely, but 80% will improve. Patients should aim to be in the 80% group that responds to treatment. It is crucial to undergo conservative treatment within the first one to two months, and if this fails, surgery should be considered promptly.
Surgery is successful in 80% of cases, but 20% of patients may not benefit. Therefore, it is ill-advised to avoid surgery in cases where conservative treatment fails, as the risk of avoiding surgery may be much greater than the risk of undergoing the procedure.
Medications for Lumbar Disc Disease Treatment
The best medications for lumbar disc disease are anti-inflammatory drugs, which should be used for at least one week. These include diclofenac, ibuprofen, meloxicam, and piroxicam in pill form. A muscle relaxant like methocarbamol or tizanidine is also often recommended. Other medications like pregabalin or gabapentin may be used to block the transmission of pain signals from the spinal cord to the brain.
In some cases, patients may ask why painkillers are prescribed. The reason is that anti-inflammatory drugs provide relief over one to two weeks, reducing inflammation. Painkillers should not be used to replace necessary surgery in conditions like appendicitis or cases where lumbar disc disease is causing paralysis.
Acupuncture in Lumbar Disc Disease Treatment
Acupuncture is another treatment method that may help improve lumbar disc disease. Like medication, acupuncture does not work for every patient, and if a herniated disc does not improve after a month of non-surgical treatments, surgery may be necessary.
Acupuncture is based on centuries of experience in countries such as China, Japan, and Korea. It is believed that applying pressure or inserting needles into specific points on the body can alleviate pain in other parts of the body. Scientific research has supported its efficacy, showing it to be effective in relieving certain types of pain.
Disc Repair for Lumbar Disc Disease
Lumbar disc disease is a common cause of back pain and sciatica, with approximately 12% of the population experiencing it at some point in their lives. In many cases, the condition improves with conservative treatments, and the disc can repair itself.
The disc may become damaged due to water loss, which can lead to cracks. Fibroblast cells in the disc's outer ring typically help repair these cracks. Anti-inflammatory medications are often prescribed to help with this healing process.
In some cases, the disc may bulge and press against nerves. Over time, biomechanical changes in the spine may help reduce the pressure inside the disc, allowing the outer ring to heal and alleviating nerve pressure.
In severe cases, if the disc ruptures and the inner material leaks out, the body’s immune cells work to reduce the protruding material. This self-repair process typically occurs within a month. If the disc does not heal by this time, surgery may be necessary.
Can Lumbar Disc Disease Be Cured?
Yes, lumbar disc disease can be cured in most cases. Approximately 80% of patients with herniated discs recover with non-surgical treatments, while 20% may require surgery. Surgery is effective when performed at the right time. However, late surgeries may yield less favorable outcomes, and delaying treatment can lead to additional damage to the spine.
Studies show that it can take anywhere from 8 to 22 months for a disc to show self-healing on MRI. Therefore, patients often prefer surgery to speed up recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the treatment methods for a lumbar disc? Treatment for a lumbar disc includes rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, injections, and in severe cases, surgery.
- What is the worst type of lumbar disc condition? The worst type is a herniated or ruptured disc, which puts pressure on the nerves, causing severe pain, muscle weakness, and limited mobility.
- How long does lumbar disc treatment take? Treatment usually takes between one to two months. If there is no improvement within this period, surgery may be considered.
- Is there a permanent cure for lumbar disc disease? No, there is no permanent cure. However, about 80% of patients fully recover with non-surgical treatments or surgery.
- Can a lumbar disc heal on its own? Yes, in many cases the disc heals gradually over time. But if recovery does not occur within a month, surgery may be necessary.